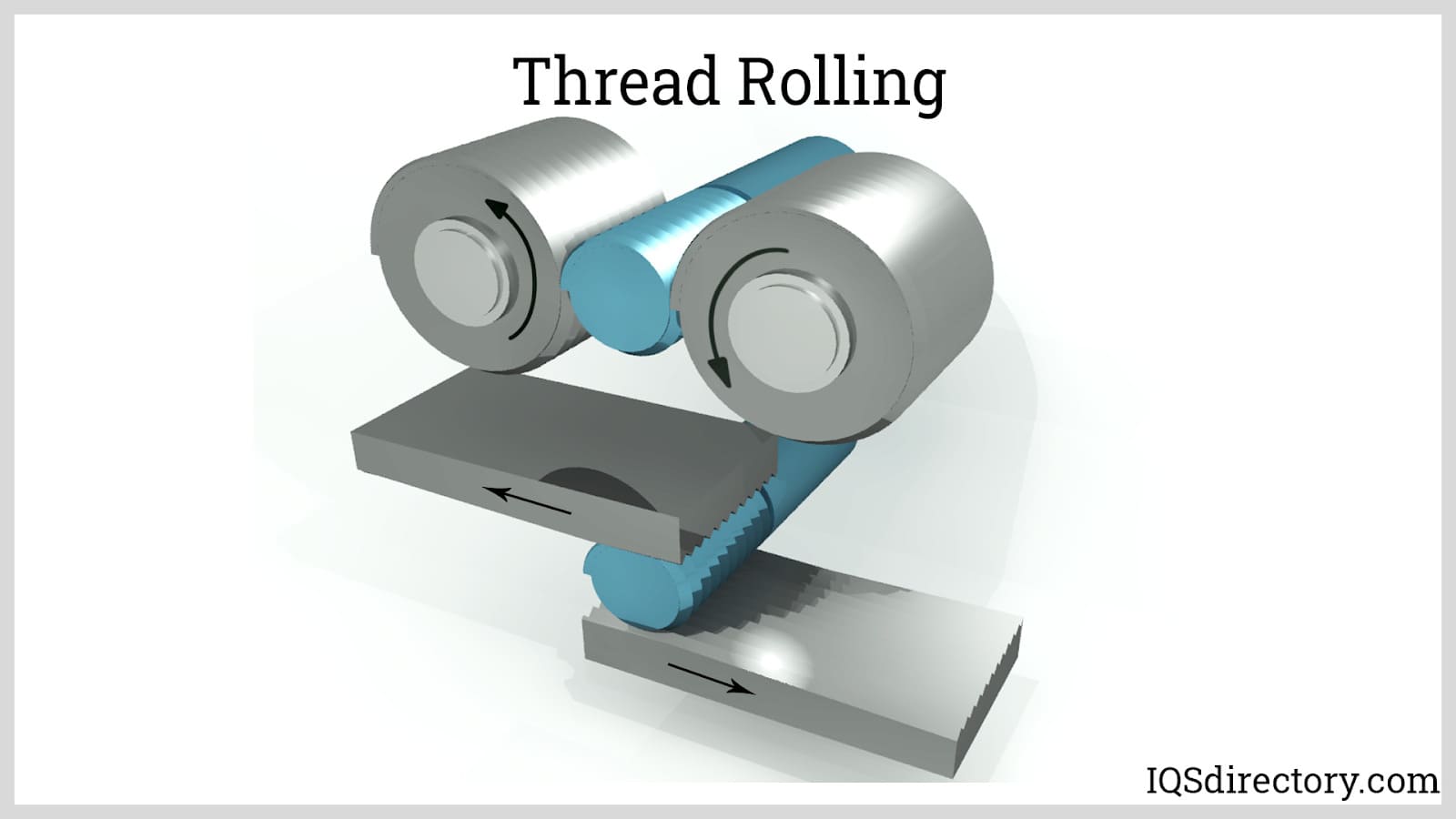
In threaded rolling, metal stock is deformed during the threading process by being rolled through dies. Using this method, external threads are created along the metal stock’s surface. The same principle, known as thread formation, can be used to create internal threads. Thread rolling is not a subtractive procedure, unlike other commonly used threading techniques like thread cutting. Stronger threads, exact final dimensions, good surface quality, and a lower coefficient of friction are just a few benefits of rolling threaded fasteners. Read More…
H & R Screw Machine Products-ISO 9001-certified manufacturer of high-volume screw machine products for many industries. We also produce CNC turned parts and provide machining of customer supplied castings, forgings and stampings.

It is Thuro’s mission to be the leading choice for screw machine parts, and to offer our products at the highest quality and the lowest cost. Our team members dedicate themselves to ensuring that our customers receive the perfect part on time, every time.

Based out of California, Pacific West America, Inc. (PWA) is a metal fabrication company. We focus most of our efforts on swiss screw machining, stampings, and precision parts, and our electronics division makes products such as cable assemblies, connectors, circuit boards and membrane switches. We create our products using a variety of CNC controlled machines, processes and robotics. Such...
At M.A.R.'s Engineering, we take great pride in our ability to deliver high-quality screw machine products. Our screw machines are capable of producing complex components with utmost precision and efficiency. Whether it's small parts or intricate assemblies, we have the expertise and equipment to meet your specific requirements. With a wide range of materials and finishes available, we can...

At GrovTec Machining, we pride ourselves on being the go-to destination for precision turned components and screw machine products. When it comes to fulfilling your machining needs, you need not look any further than our state-of-the-art screw machine shop. Our dedicated team of experienced machinists and cutting-edge equipment allow us to tackle projects of all sizes and complexities.

Dynamic Machining X Manufacturing, LLC is a leading provider of precision machining services, specializing in medical machining, aerospace parts manufacturing, mill-turn center operations, 5-axis machining, and more. Our state-of-the-art facilities and highly skilled team enable us to deliver complex and intricate components with unparalleled accuracy and quality. Serving a wide range of...

At Lakeside Screw Products, we pride ourselves on delivering exceptional screw machine products crafted with precision and quality. Our commitment to excellence is ingrained in our rigorous quality control process, ensuring that every component we produce meets the highest standards of accuracy and reliability. Since 1977, Lakeside Screw Products has been a trusted partner, providing unparalleled ...

More Threaded Rolling Manufacturers
Threaded fasteners produced through thread rolling are non-permanent couplings that can be mechanically loosened or disassembled. Lead screws and power screws are categorized as mechanical drives or mechanisms. These machine components deliver electricity to other machine sections while regulating movement.

Thread Rolling Processes
There are three main categories for thread generation processes:
- Deformation
- Subtractive
- Additive
The way the thread is created or shaped varies between these. For example, cutting procedures are more commonly used to describe subtractive processes.
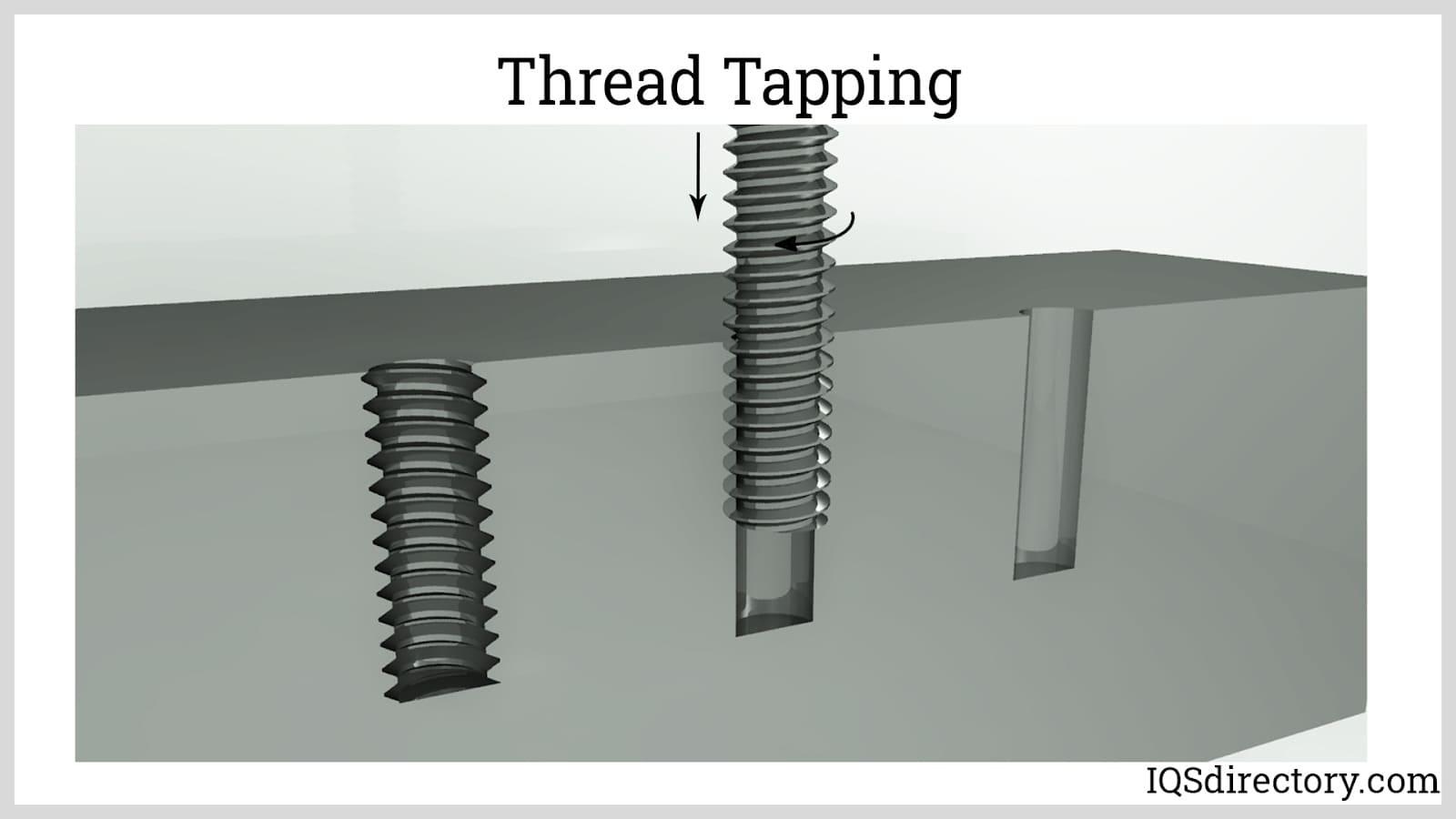
Thread Tapping
Internal threads are created through the thread machining procedure of tapping. This uses a cylindrical tap, or conical cutting instrument. The many cutting edges on the tap resemble an external thread.
The tap is rotated while being axially advanced farther into the metal stock's bore to produce the internal thread.
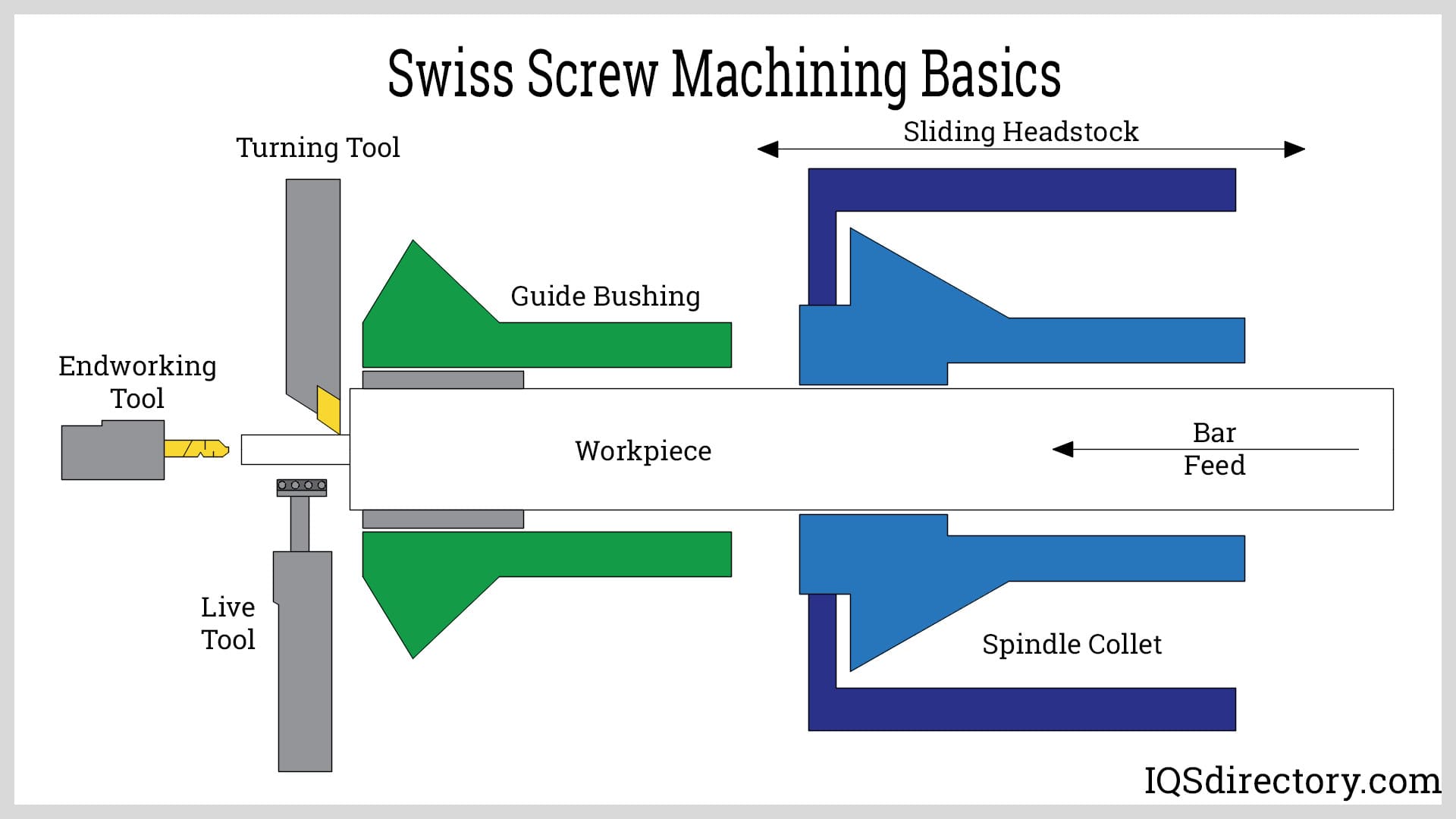
Single-point Cutting
Single-point cutting uses a lathe machine, where the metal stock is clamped and rotated. A carriage fed linearly by a lead screw positions the cutting tool. This procedure can create both internal and external threads.
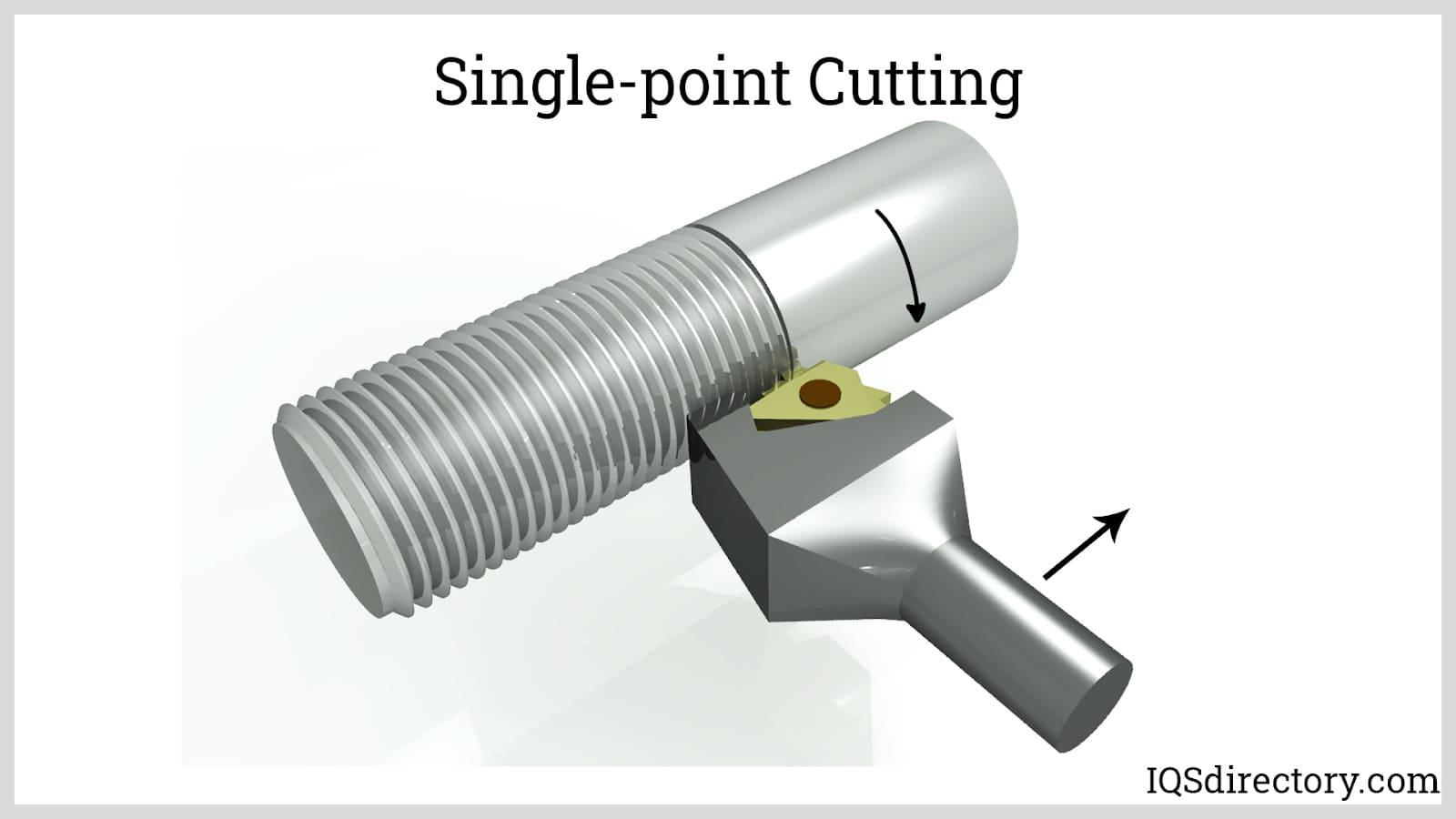
Compared to tapping or die-cutting, this procedure takes longer. It has the benefit of producing several threads with just one cutting tool.
Die Threading
This method is employed to create external threads. It uses a similar degree of force and cutting motion to tapping. The metal stock is cut using a die, with several cutting points that resemble internal threads. Several die designs can be self-opening or solid.
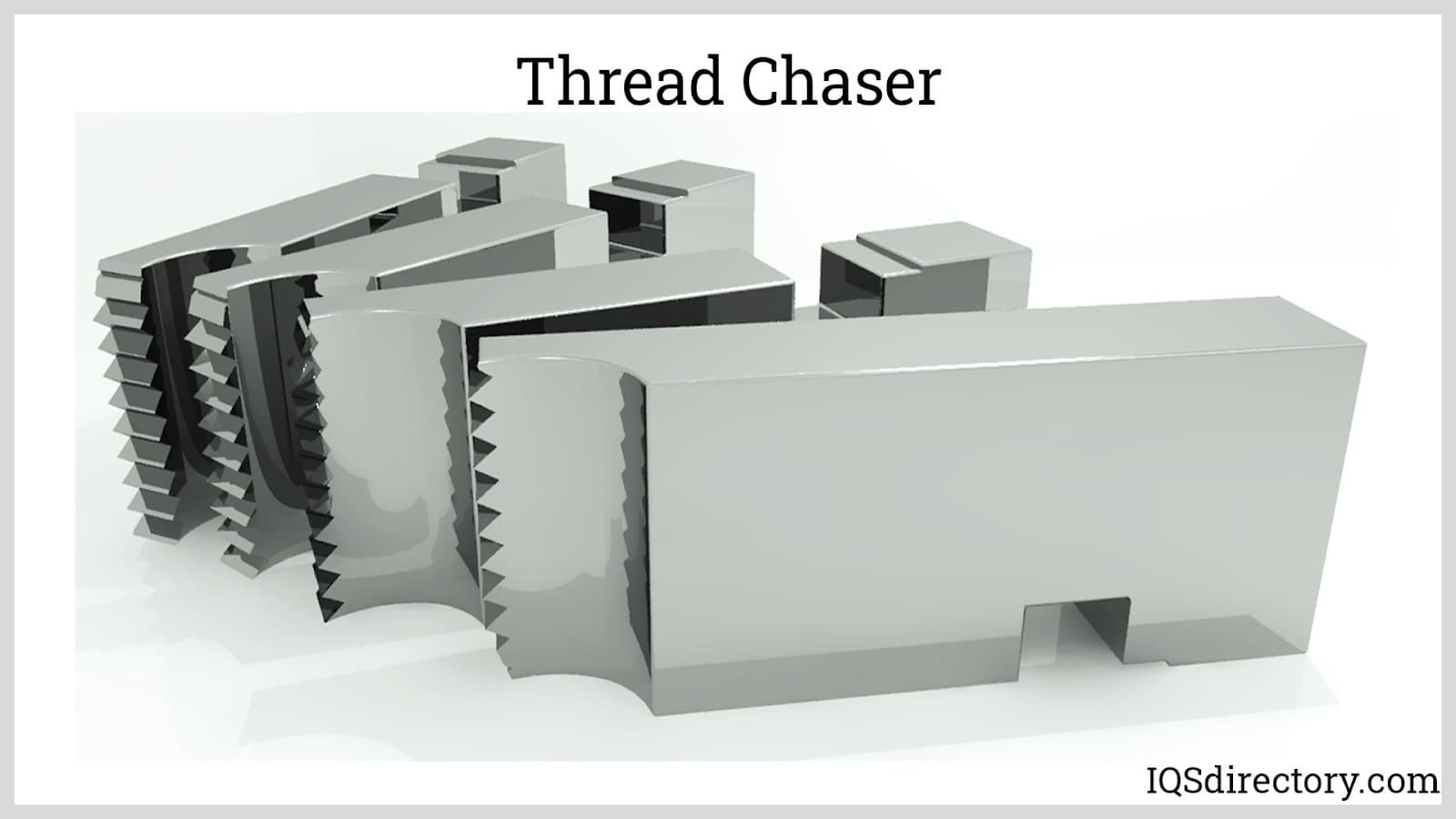
Thread Chasing
Chasing uses a thread chaser, a collection of assembled single-point cutting tools. To cut the thread, a chaser is commonly attached to a lathe's carriage that is gradually indexed.
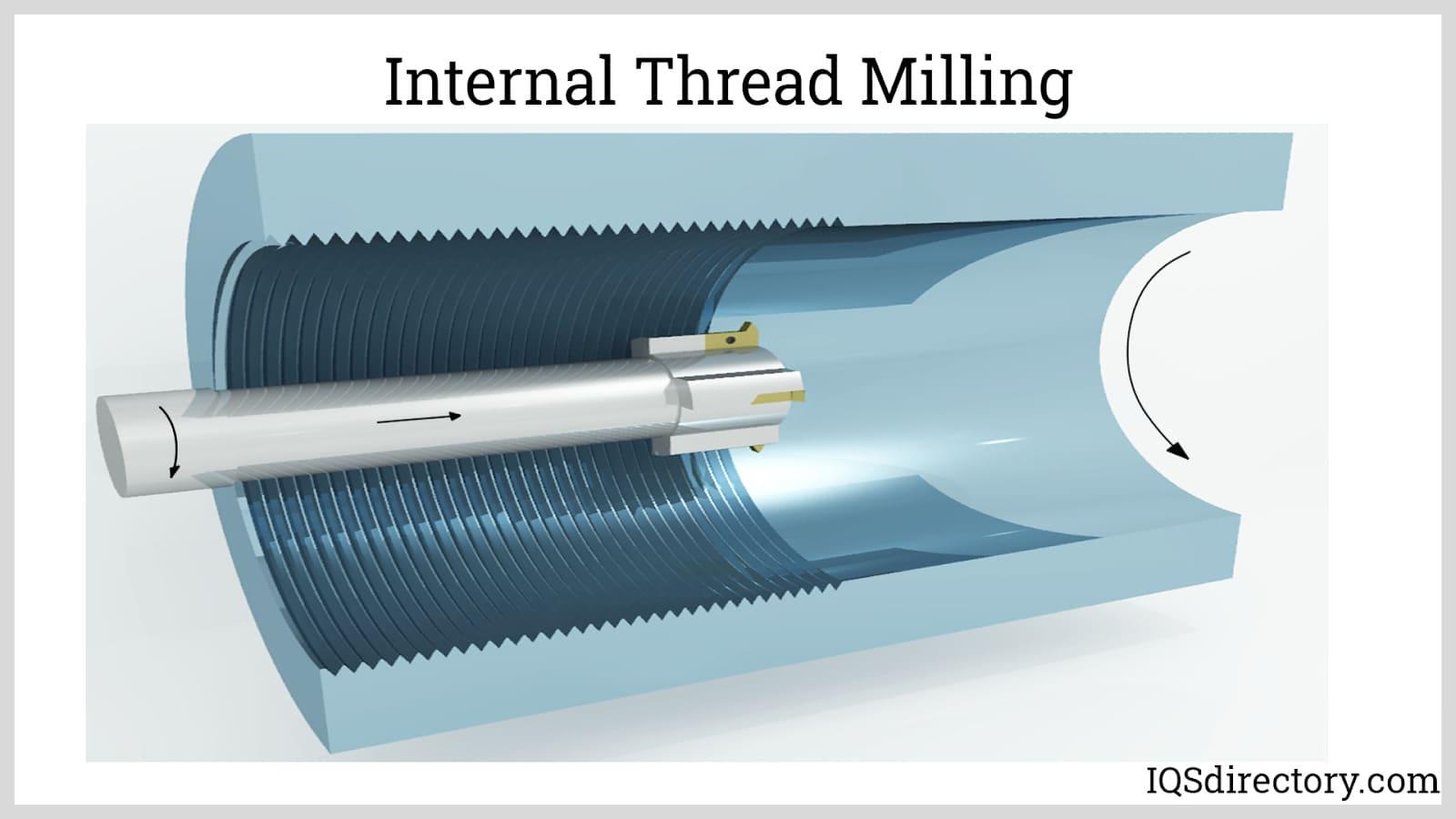
Thread Milling
During the milling procedure, the stock is threaded using one or more rotary cutting tools. The cutting tool is not only rotated and indexed axially, as in tapping and die-threading, but it also revolves around the perimeter of the threaded surface. Internal and external threads can both be produced via thread milling.

Thread Casting
In this operation, the molten metal is injected or poured into a die or mold. The threaded part's negative form is contained in the die. To create precise threads, this procedure needs further machining operations. Therefore, fine threads cannot be produced with this method.
Advantages of Thread Rolling
Using a rolled screw press product has both many benefits and drawbacks. The product's stronger finish and dimensional correctness are thread rolling's key benefits. However, this technique relies on metal deformation. Therefore, it can only be used on soft metals and has higher tooling costs.
High Thread Strength
Thread rolling is known as a cold working procedure since it is often carried out at relatively low temperatures. It is well known that cold working can create stronger parts without additional heat treatment. Rolling is a good threading method for materials that don't respond to heat treatment. Compared to cut or ground threads, rolled threads are 10–20% stronger.
Good Surface Finishes
Without requiring further polishing steps, thread rolling naturally produces smooth and burnished threads. Any unevenness on the thread's surface is removed by the strong compressive forces that distort the metal. Cut threads normally have a surface roughness of 64 to 125 micro-inches Ra, whereas rolled surfaces typically have a surface roughness of 8 to 24 micro-inches Ra. Additionally, rolled threads are free of burrs, chatter marks, tears, and cutting marks.
Precision Threading
Since no material is removed from the stock during the rolling thread process and the dies used are mirror images of threads to be manufactured, the procedure may produce parts with high precision and accuracy over an extended period. This is true as long as the dies are precise and produced with enough hardness.

Disadvantages of Thread Rolling
Expensive Tooling
Rolling dies must be exact and firm. Thread dimensional precision will be poor if the die is deformed. In addition, the needed hardness makes it challenging to fabricate the dies precisely.
Not Suitable for Hard Materials
Most thread rolling is done using malleable metals. Although feasible, thread rolling is not performed for metals with a Rockwell hardness greater than 40. Thread grinding is more useful above this hardness level. In addition, tool life is markedly decreased while rolling hard materials.
Choosing the Right Thread Rolling Company
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when selecting a thread rolling company, it is important to compare 5 companies using our thread rolling directory. Each thread rolling company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each thread rolling company website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple thread rolling companies with the same form.








 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services